A non-peer reviewed pre-print paper attempts to provide data to support the ongoing theory that increased temperature reduced transmission of SARS-CoV-2, although there has been no major evidence to support it completely.
Abstract
Seasonal temperature variation may impact the trajectories of COVID-19 in different global regions. Cumulative data reported by the World Health Organization, for dates up to March 27, 2020 1 , show association between COVID-19 incidence and regions at or above 30o latitude. Historic climate data also show significant reduction of case rates with mean maximum temperature above approximately 22.5 degrees Celsius. Variance at the local level, however, could not be well explained by geography and temperature. These preliminary findings support continued countermeasures and study of SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19 transmission rates by temperature and humidity.
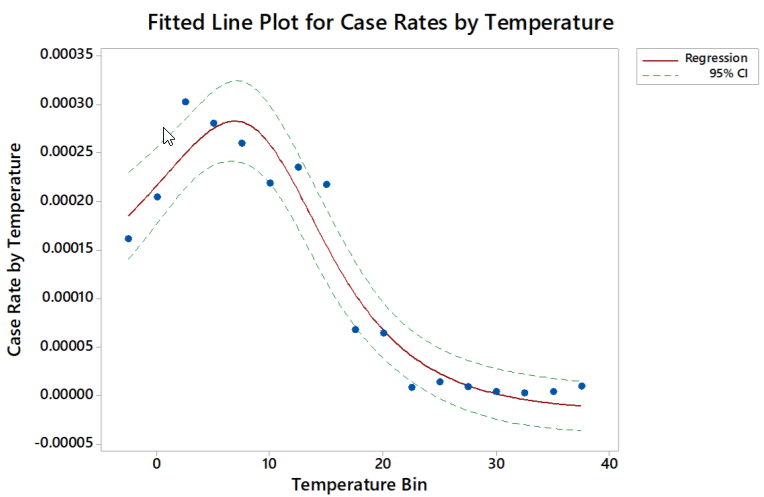
https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.04.02.20051524v1.full.pdf
doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.04.02.20051524